More Search Results...
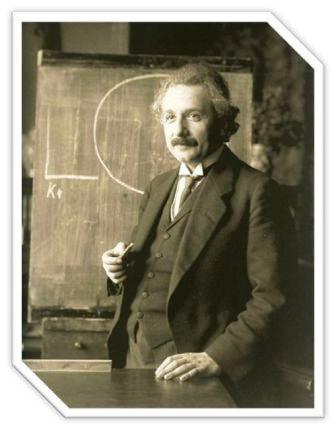
Albert Einstein [Germany] (14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who developed the general theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics (alongside quantum mechanics). While best known for his mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2 (which has been dubbed “the world’s most famous equation”), he received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics “for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect”. The latter was pivotal in establishing quantum theory.
Relativity
Near the beginning of his career, Einstein thought that Newtonian mechanics was no longer enough to reconcile the laws of classical mechanics with the laws of the electromagnetic field. This led to the development of his special theory of relativity. He realized, however, that the principle of relativity could also be extended to gravitational fields, and with his subsequent theory of gravitation in 1916, he published a paper on the general theory of relativity. He continued to deal with problems of statistical mechanics and quantum theory, which led to his explanations of particle theory and the motion of molecules. He also investigated the thermal properties of light which laid the foundation of the photon theory of light. In 1917, Einstein applied the general theory of relativity to model the large-scale structure of the universe.
More info →The Meaning of Relativity: “With Four Diagrams”
The theory of relativity is intimately connected with the theory of space and time. I shall therefore begin with a brief investigation of the origin of our ideas of space and time, although in doing so I know that I introduce a controversial subject. The object of all science, whether natural science or psychology, is to co-ordinate our experiences and to bring them into a logical system. How are our customary ideas of space and time related to the character of our experiences?
The experiences of an individual appear to us arranged in a series of events; in this series the single events which we remember appear to be ordered according to the criterion of “earlier” and “later”, which cannot be analysed further.
More info →The Principle of Relativity: (Original Papers)
HISTORICAL INTRODUCTION
Einstein's first paper on the restricted 'Theory of Relativity', originally published in the 'Annalen der Physik' in l905. Translated from the original German Papers by Dr. Meghnad Saha
Lord Kelvin writing-in 1893, in his prefaceto the English edition of Hertz's Researches on Electric Waves, says" many workers and many thinkers have helped to build up the nineteenth century school of plenum, one ether for light, heat, electricity, magnetism; and the German and English volumes containing Hertz's electrical papers, given to th
More info →